1127 ZigZagging on a Tree (30分)
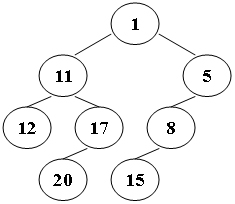
Suppose that all the keys in a binary tree are distinct positive integers. A unique binary tree can be determined by a given pair of postorder and inorder traversal sequences. And it is a simple standard routine to print the numbers in level-order. However, if you think the problem is too simple, then you are too naive. This time you are supposed to print the numbers in "zigzagging order" -- that is, starting from the root, print the numbers level-by-level, alternating between left to right and right to left. For example, for the following tree you must output: 1 11 5 8 17 12 20 15.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line gives a positive integer N (≤30), the total number of nodes in the binary tree. The second line gives the inorder sequence and the third line gives the postorder sequence. All the numbers in a line are separated by a space.
Output Specification:
For each test case, print the zigzagging sequence of the tree in a line. All the numbers in a line must be separated by exactly one space, and there must be no extra space at the end of the line.
Sample Input:
8
12 11 20 17 1 15 8 5
12 20 17 11 15 8 5 1
Sample Output:
1 11 5 8 17 12 20 15
题目描述:已知中序遍历和后序遍历可以得到唯一的二叉树;已知中序遍历和先序遍历,可以得到唯一的二叉树。现在题目给出中序和后序遍历,需要求出层序遍历的结果。但是这个层序遍历需要按照Z字行输出。
解题思路:不需要建树,递归就能得到层序遍历的结果。1086题解解释了已知先序遍历和中序遍历,求后序遍历的结果,思路与这题差不多,可以参考。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int n, cnt;
const int maxn = 1e4+5;
vector<int> inorder, post;
vector<int> level[maxn];
void get_level(int root, int inl, int inr, int index){
if(inl>inr) return ;
int i = inl;
cnt = index;
level[index].push_back(post[root]);
while(i<=inr&&inorder[i]!=post[root]) i++;
get_level(root-(inr-i+1),inl,i-1,index+1);
get_level(root-1,i+1,inr,index+1);
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d", &n);
inorder.resize(n);
post.resize(n);
for(int i=0; i<n; i++) scanf("%d", &inorder[i]);
for(int i=0; i<n; i++) scanf("%d", &post[i]);
get_level(n-1,0,n-1,1);
for(int i=1; i<=cnt; i++){
if(i%2==0){
for(int j=0; j<level[i].size(); j++){
if(i!=1) printf(" ");
printf("%d", level[i][j]);
}
}
else{
for(int j=level[i].size()-1; j>=0; j--){
if(i!=1) printf(" ");
printf("%d", level[i][j]);
}
}
}
return 0;
}