1135 Is It A Red-Black Tree (30分)
There is a kind of balanced binary search tree named red-black tree in the data structure. It has the following 5 properties:
- (1) Every node is either red or black.
- (2) The root is black.
- (3) Every leaf (NULL) is black.
- (4) If a node is red, then both its children are black.
- (5) For each node, all simple paths from the node to descendant leaves contain the same number of black nodes.
For example, the tree in Figure 1 is a red-black tree, while the ones in Figure 2 and 3 are not.
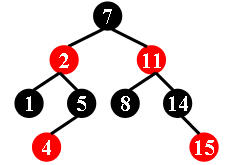 |
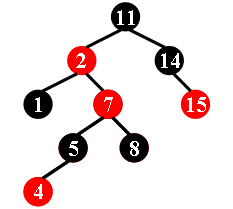 |
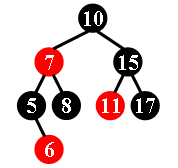 |
|---|---|---|
| Figure 1 | Figure 2 | Figure 3 |
For each given binary search tree, you are supposed to tell if it is a legal red-black tree.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains several test cases. The first line gives a positive integer K (≤30) which is the total number of cases. For each case, the first line gives a positive integer N (≤30), the total number of nodes in the binary tree. The second line gives the preorder traversal sequence of the tree. While all the keys in a tree are positive integers, we use negative signs to represent red nodes. All the numbers in a line are separated by a space. The sample input cases correspond to the trees shown in Figure 1, 2 and 3.
Output Specification:
For each test case, print in a line "Yes" if the given tree is a red-black tree, or "No" if not.
Sample Input:
3
9
7 -2 1 5 -4 -11 8 14 -15
9
11 -2 1 -7 5 -4 8 14 -15
8
10 -7 5 -6 8 15 -11 17
Sample Output:
Yes
No
No
题目描述:红黑树是一个二叉搜索树,根节点的值大于左子结点,根节点的值小于或等于右子节点的值。红黑树的特点如下:
1)每一个结点由红色或黑色组成
2)根节点为黑色
3)每个叶子节点(NULL)都为黑色
4)如果节点为红色,那他的两个子结点必须为黑色
5)根节点到每个子结点的路径中,黑色子结点的个数都要相同
输入:第一行k为测试用例数,往下有k组;每组第一行n为结点总数,每组第二行有n个数,表示需要插入的结点的值,正整数为黑色,负整数为红色。
输出:输出是否能构成红黑树,是为Yes,否为No。
解题思路:先构建一个红黑树,将题目给定的值依序插入就能将二叉搜索树构建出来,我是通过递归的方法构建的。树构建完成后,用BFS遍历每个结点,检查是否符合红黑树的特性。
注意:题目给出的结点值都不是叶子结点,叶子节点没有值为NULL,这是个坑,没注意到测试点2、3就会错。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int n, m, cnt;
bool flag;
struct node{
int num;
node *l, *r;
node(){
l = r = NULL;
}
};
node *Insert(node *root, int k){
if(root==NULL){
root = new node();
root->num = k;
root->l = root->r = NULL;
}
else if(abs(k)>=abs(root->num)){
root->r = Insert(root->r,k);
}
else root->l = Insert(root->l,k);
return root;
}
void bfs(node *root){
pair<node*,int> t, tt;
node *troot;
queue<pair<node*,int>> q;
t.first = root; t.second = 0;
q.push(t);
while(!q.empty()&&flag){
t = q.front(); q.pop();
troot = t.first;
if(troot==NULL){
t.second++;
if(cnt==-1) cnt = t.second;
if(cnt!=t.second) flag = false;
continue;
}
if(troot->num>0) t.second++;
if(troot->l!=NULL&&troot->num<0&&troot->l->num<0) flag = false;
tt.first = troot->l; tt.second = t.second;
q.push(tt);
if(troot->r!=NULL&&troot->num<0&&troot->r->num<0) flag = false;
tt.first = troot->r; tt.second = t.second;
q.push(tt);
}
}
int main()
{
int k;
scanf("%d", &n);
for(int i=0; i<n; i++){
scanf("%d", &m);
node *tree = NULL;
for(int j=0; j<m; j++){
scanf("%d", &k);
tree = Insert(tree,k);
}
flag = true;
cnt = -1;
if(tree->num<0) flag = false;
else bfs(tree);
if(flag) printf("Yes\n");
else printf("No\n");
}
return 0;
}